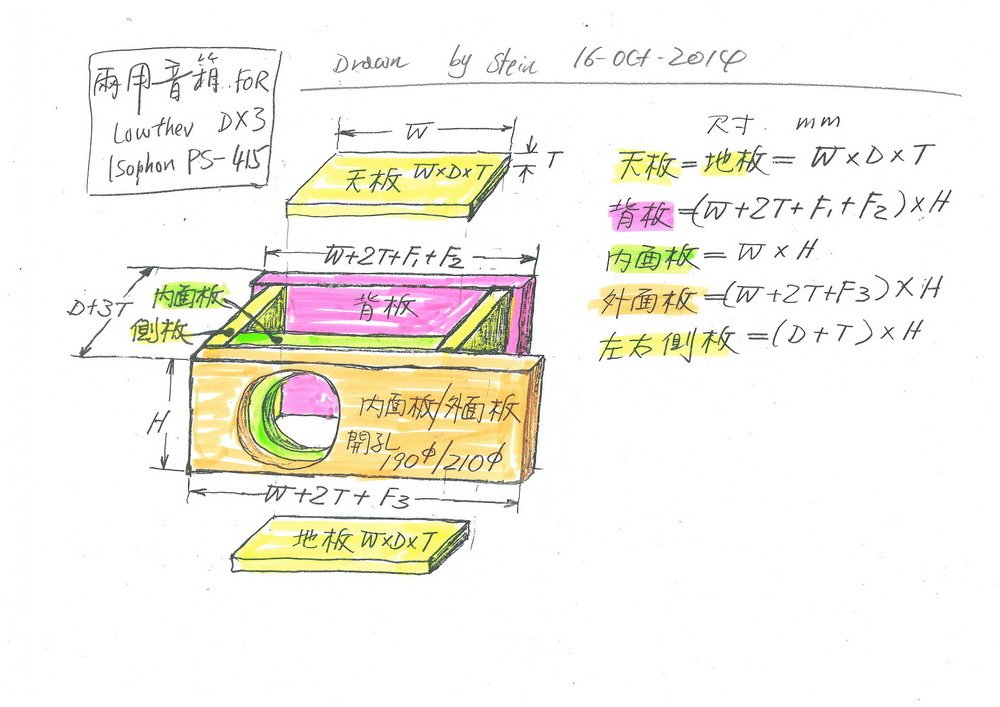
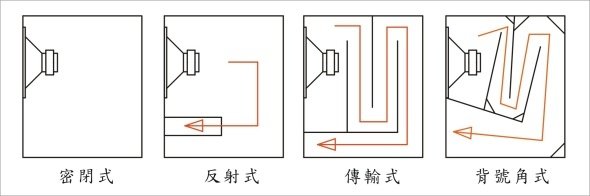
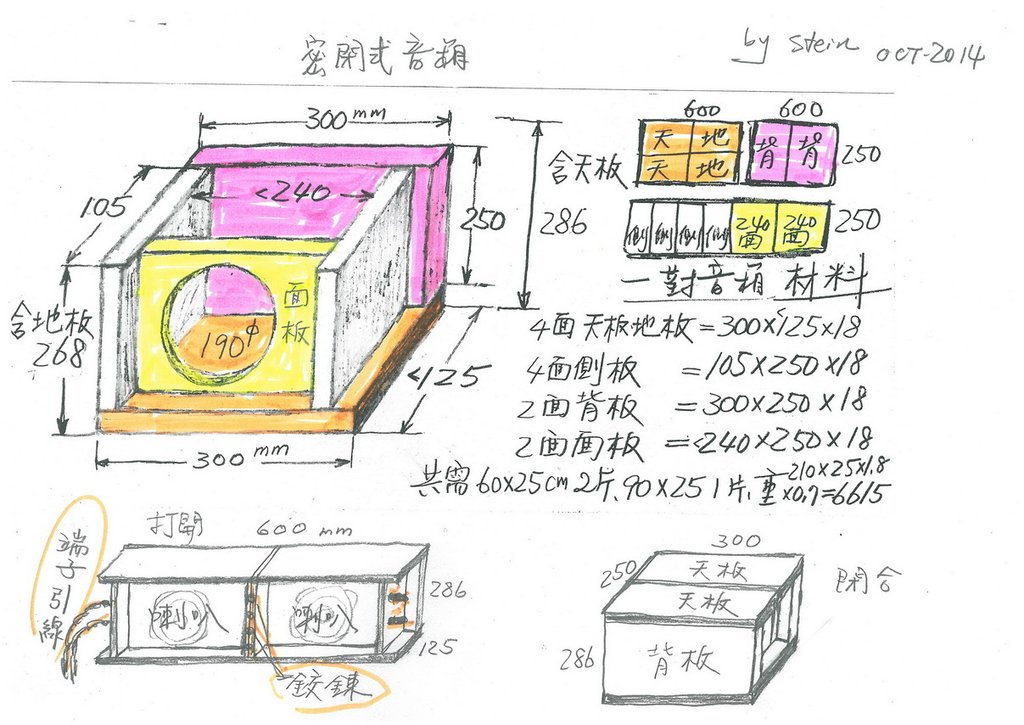
想做一對密閉式音箱,碰到兩個不成問題的問題。
1.
單體振膜一定是完美的隔離前後空氣,有密閉的效果嗎?
像是 防塵蓋 一定是氣密的嗎?
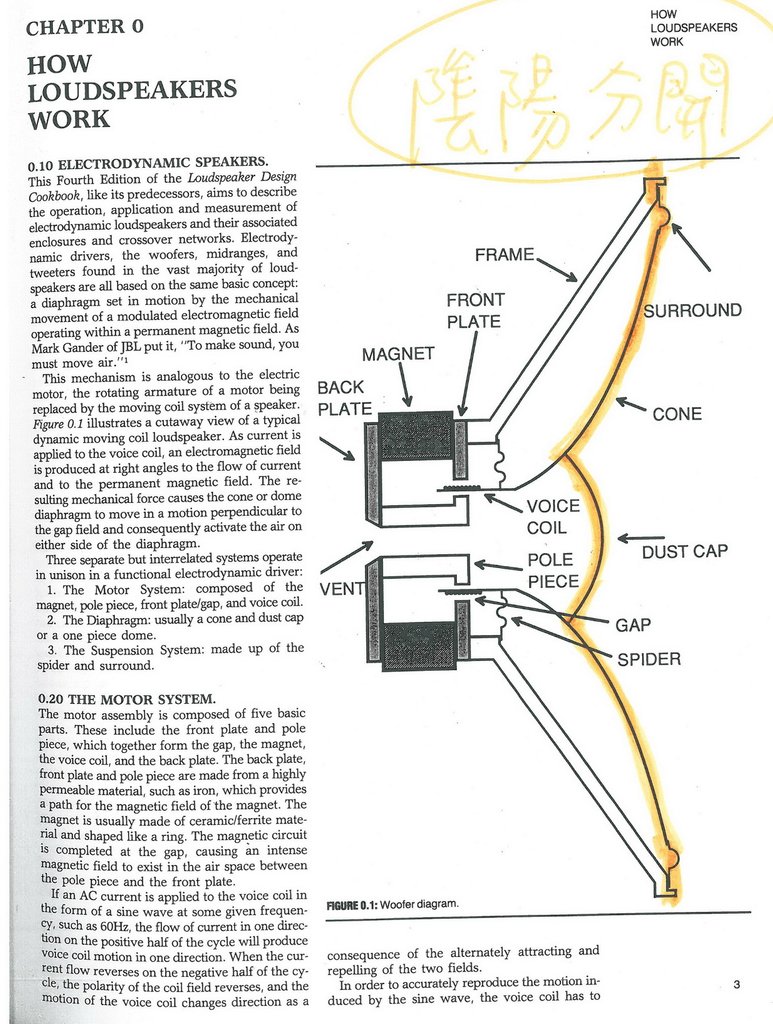

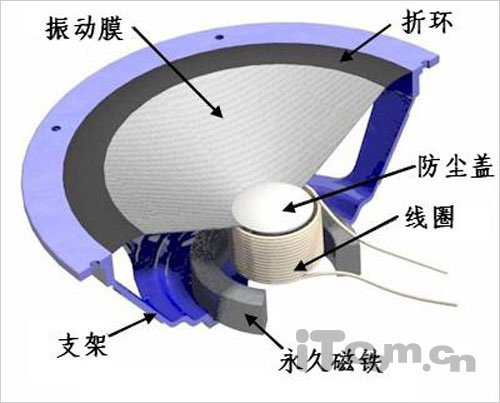
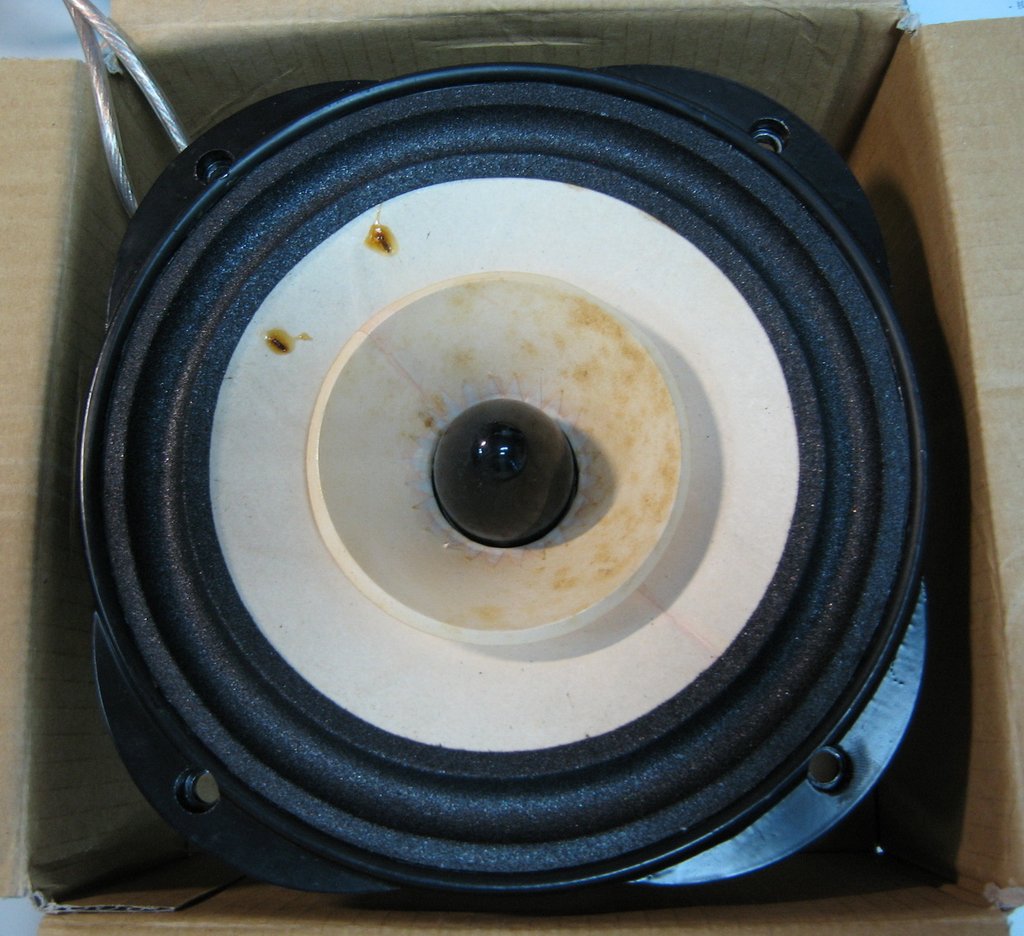
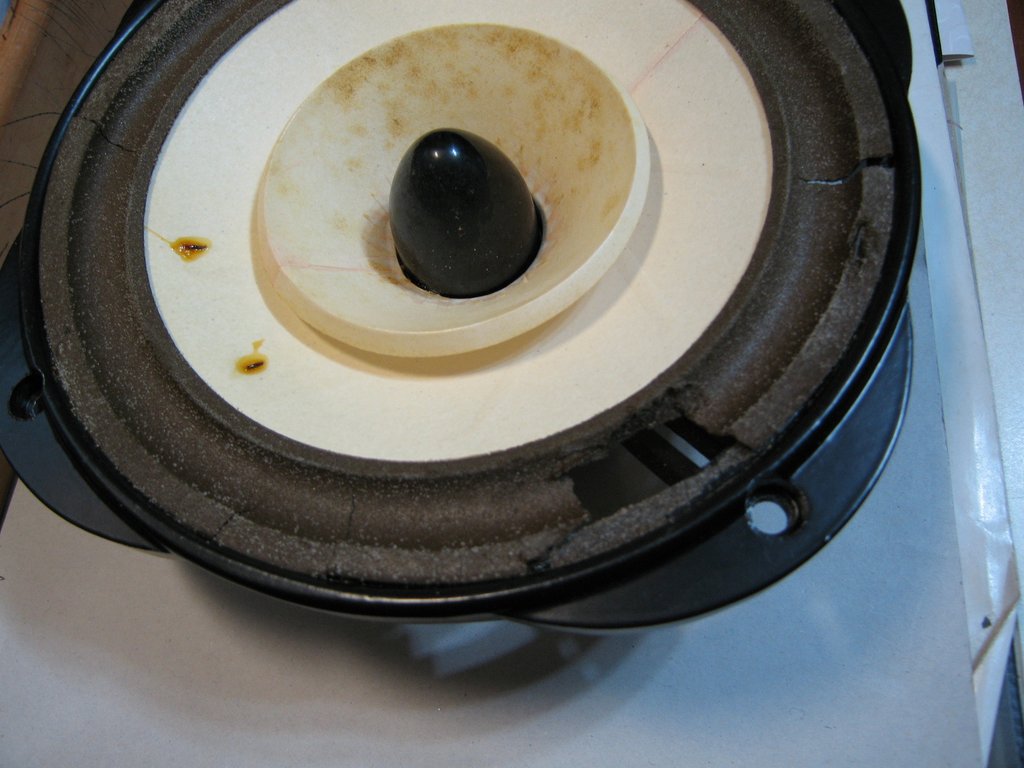
像是這個角錐會破壞氣密嗎?
角錐是鎖定在磁鐵上,振膜沒有防塵蓋,所以不會是完全氣密的。


2.
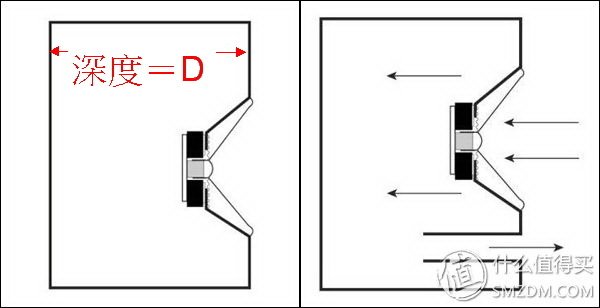
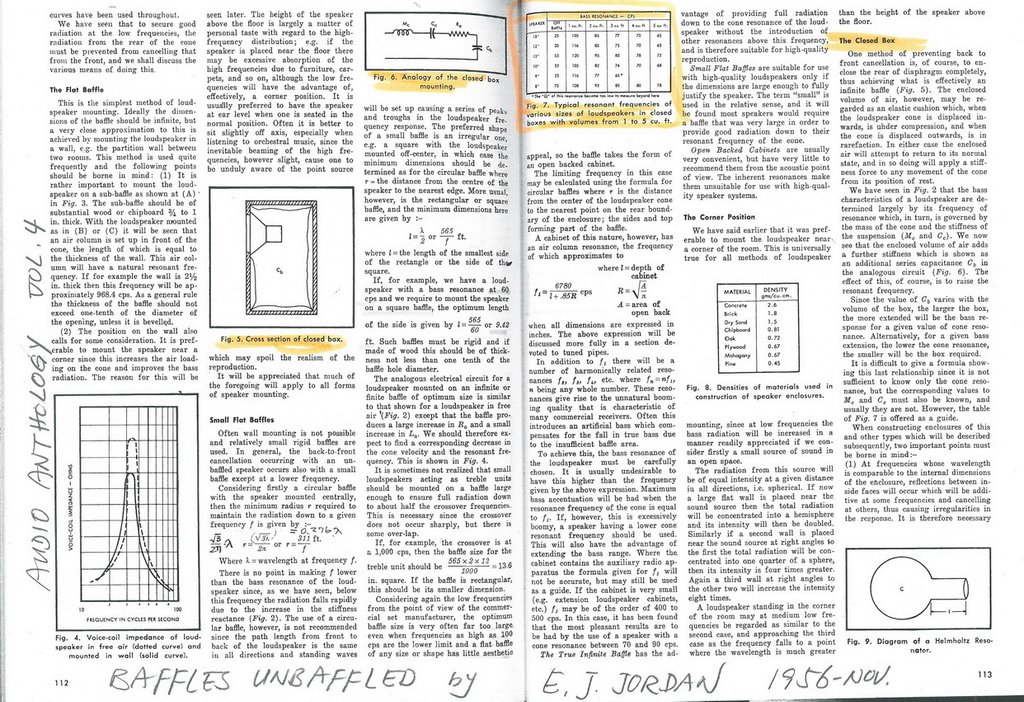
密閉音箱當然是要密不通風,內外完美隔離的,否則不叫 密閉。
根據氣體 查理定律,箱體內的空氣,壓力維持不變,即是箱體內外的空氣壓力一樣之下,溫度變化 1 度 C,熱漲冷縮,體積會變化 273分之一。
箱體既然是剛性的,只好推動振膜,前移 或是 後縮,箱內的空氣體積才能變化應對。
冬天比對夏天,或者 沒開機之前比對熱機幾個鐘頭之後,箱內的空氣溫度不會是一成不變的。
方便計算起見,以變化 10 度 C為例,箱內的空氣體積會變化 10*1/273=1/27=0.037= 百分之3.7
再方便計算起見,以音箱面板的面積是 振膜的面積的 2.7倍為例,振膜要比面板 位移2.7倍。
則振膜,也就是線圈跟磁鐵 的相對位置; 需要前後位移是:
箱內深度 D乘上 0.037*2.7=0.1= D的百分之 10.
D= 100 mm 時,振膜位移 10 mm
D= 200 mm 時,振膜位移 20 mm
靜態之下,振膜、線圈這樣 10 mm-20 mm 的位移可以接受嗎?
前後位移 可以看成電路上 3極真空管放大的Bias變更。
3.
密閉音箱要是拿到阿里山高山,氣壓低,溫度低,會是怎樣的位移?
4.
總結的疑問是:
箱體要做到密不透氣嗎?
喇叭接線端子也要密不漏氣嗎?
還是要加上一個 保特瓶蓋,可以隨時 <換氣>?
Wik對這疑問 有解答:
要 <微漏> 才可以
The enclosure or driver must have a small leak so internal and external pressures can equalise over time
因此用有孔的 香蕉插 喇叭接線端子 剛好。
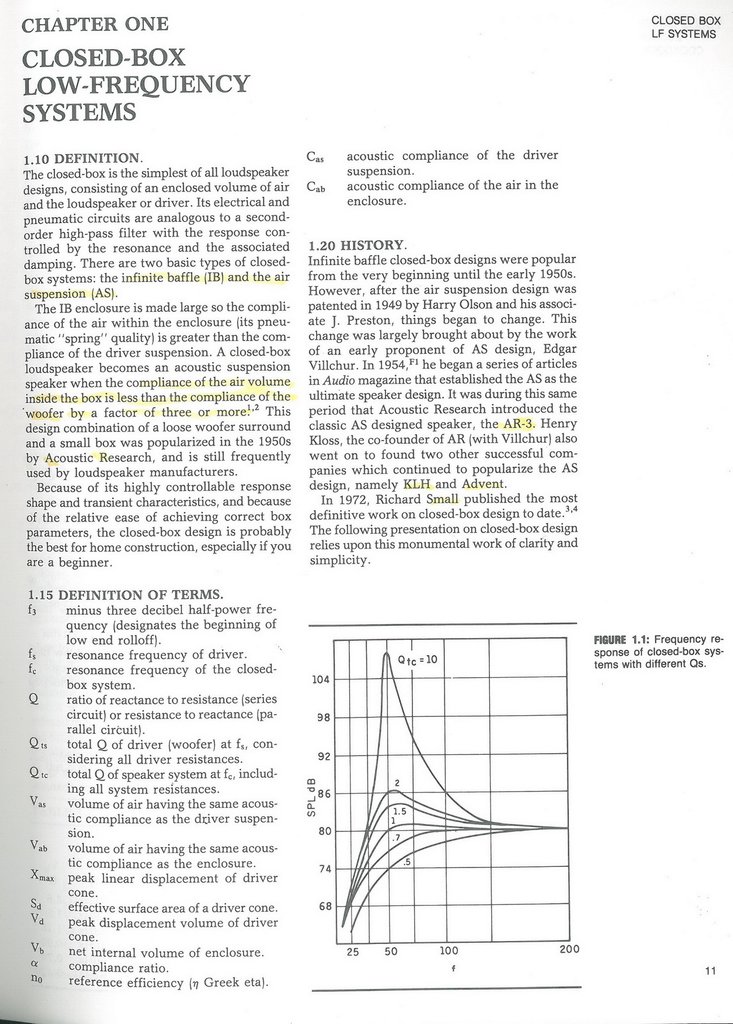
Sealed (or closed) enclosures
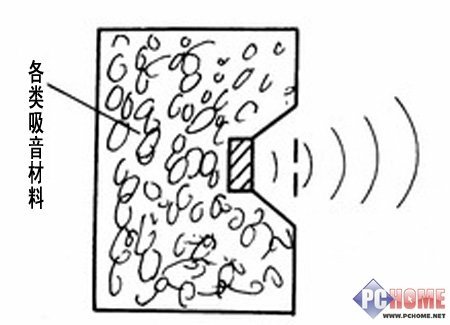
The loudspeaker driver's moving mass and compliance (slackness or reciprocal stiffness of the suspension) determines the driver's resonant frequency. In combination with the damping properties of the system (both mechanical and electrical) all these factors affect the low-frequency response of sealed-box systems. Output falls below the system's resonant frequency (Fs), defined as the frequency of peak impedance. In a closed-box, the air inside the box acts as a spring, returning the cone to the 'zero' position in the absence of a signal. A significant increase in the effective volume of a sealed-box loudspeaker can be achieved by a filling of fibrous material, typically fiberglass, bonded acetate fiber (BAF) or long-fiber wool. The effective volume increase can be as much as 40% and is due primarily to a reduction in the speed of sound, and not to the popular misconception of a change in operating conditions from adiabatic to isothermal. The enclosure or driver must have a small leak so internal and external pressures can equalise over time, to compensate for barometric pressure or altitude; the porous nature of paper cones, or an imperfectly sealed enclosure, is normally sufficient to provide this slow pressure equalisation.
Types of Speaker Enclosures: Sealed and Ported
8 of 11 in Series: The Essentials of Speakers
The speaker enclosure (typically, a box) is critical in a home theater system. There are two major types of speaker enclosures, sealed and ported. Either way, a speaker enclosure should handle vibrations with ease and add little sound interference to the sound emanating from the speaker drivers.

With all the shaking that speaker drivers do, if you have a flimsy speaker encasement, it’s going to make a lot of noise, fall apart, or both.
-
Sealed (or acoustic suspension) enclosures: A sealed enclosure is an airtight case. As your driver moves back and forth, the air pressure in the speaker constantly changes. This puts extra pressure from behind on the diaphragm as it moves in and out, and that takes extra power to overcome. On the positive side, that extra pressure makes the cone snap back and forth faster and with more precision, giving you a crisper, more accurate sound.
-
Ported (or bass reflex) enclosures: In the front of this enclosure is a hole (port) that equalizes pressure between the inside and outside of the speaker. When the diaphragm moves back into the speaker, it increases the internal pressure, which is funneled out through the front port of the speaker. This action augments the sound waves traveling from the speaker, and increases the efficiency tremendously.
The downside of a ported enclosure is that you may get less accurate results from a reproductive sound perspective. That’s because a ported enclosure doesn’t have the benefit of the extra pressure influencing the reverberating diaphragm. So the speaker sound might reproduce bass notes less precisely — substituting a louder boominess for a more realistic reproduction of the low notes.
Ported enclosures can dramatically decrease your power requirements because they increase the bass output of a speaker by around 3 dB compared to a sealed enclosure. To match a 3 dB output boost through amplification, the power applied to the speaker needs to be doubled. So if a bass reflex enclosure speaker was powered with a 150-watt amplifier, a sealed enclosure speaker would require a 300-watt amplifier to produce the same output.
In the end, you can be happy with either sealed or ported designs. Just keep in mind that these units handle bass differently and that good design and construction can minimize problems associated with either speaker design.




 留言列表
留言列表
